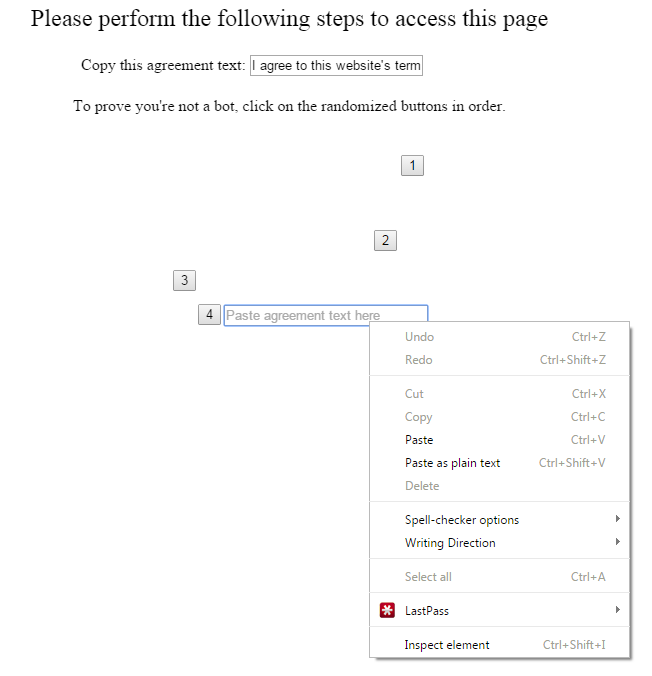
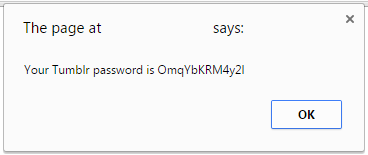
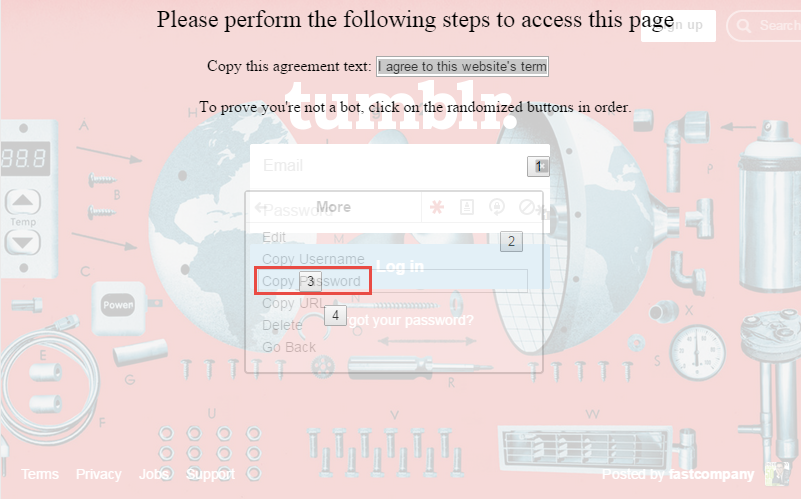
Your blog is one of the most important things in the world to you. It is the way that you communicate with the outside world, share your passions, and potentially even make your income.
There are other people out there who do not feel the same way.
These hackers want to take your blog and use it for profit by either spamming ad-filled posts on your blog or using your subscriber lists for their criminal purposes.
If your blog is taken over by a hacker, not only might you lose your blog, you might lose some of your readership and your reputation. It is worth any inconvenience to make sure this doesn’t happen.
The Basics
What goes for the rest of the internet doesn’t change for your blog. Many of the threats to your computer can affect your blog as well, so you have to maintain a constant vigilance on both fronts. Know these basics and know them well.Passwords and Usernames
While it may be convenient for you to have a simple password such as “Password123” or something similar, hackers will be able to crack such a password in five minutes on a slow day. You need something better with different types of characters, no words in the dictionary, and enough characters to keep the number of possibilities high (at least 10). Once you commit a good one to memory, you won’t care so much about the hassle, and it will get easier to remember a new one each time you change it.If you are looking for some examples of what a good password looks like, check out the listed examples below:
- Typ561Rvsert?
- M0O0Nrare!
- J0hnsm1TH
- !Pra531cTiCal
Many different exploits and attacks hackers use will start on the premise that Admin is a username or profile name on the website, so if you’re using it you’ve made their job a lot easier. Other than this, just make sure not to hand your username out to everyone. Keep it as safe as your password.
Security Software
Your computer is linked to your blog, and there is nothing you can do to change that. If your computer is attacked, consider your blog attacked as well. Any cookies or saved passwords on your device could be stolen and used to gain access to your blog.You need security software on all of your devices, and you need to make sure it is updated consistently. There are both free programs and premium programs available. Some of the better free products include Panda Free Antivirus, AVG Free Antivirus, and Avira. Some of the best premium programs and brands include Norton, McAfee, and Kaspersky Total Security.
Each have their benefits and disadvantages (for example, Kaspersky is the most expensive, but has every feature you could want), and you will have to decide what is in your budget and most compatible with your needs. Consider it an investment in your blog’s survival.
Email Security
Where your blog is concerned, your email security is of equal importance to your general computer security. If a hacker manages to get into your email account, they can pretty easily find your password and/or your username. This is in addition to the many other problems you will have to deal with when your email is hacked (such as potential identity theft).This is why your email should be the most protected account you have. If you are particularly cautious, you will want to create a separate email for blogging purposes. You can also use it as a separate contact point for readers so you can more easily organize your emails. A second email address is free and easy to start, so there is no disadvantage to setting one up (other than time).
In addition to this, you will want a strong password (see the tips outlined earlier). Your email account might also have other verification options such as a security image or security question you have to answer whenever you log in on a new device. Take any and all of these options, and note that you don’t have to share your email with everyone you meet.
Platforms, Tools, and Plugins
A strong webpage is your first line of defense against potential hackers. Hackers aren’t necessarily lazy, but they are opportunistic and will attack the weakest blog they see. If your blog looks dated, it’s security is probably dated, too. Try to think how a predator thinks, and then take measures that will ward them off. Try to do this from a holistic viewpoint, taking into consideration the platform, the base blog, and any plugins you have installed.Security Tools and Add-ons
Most blogging platforms, WordPress especially among them, have a lot of tools and plugins available to users in order to make your website more secure. Let us take a look at some of the most popular and useful ones:- Acunetix WP Security Scan is one of the first plugins you should download for your blog. Once activated, it will scan your blog and design for any potential security holes and then recommend fixes for you. It is continually improving and is a great introduction to WordPress security.
- WordFence is likely the most popular and well-known of all the plugins for WordPress right now. The plugin scans the coding of your website, then optimizes your security and allegedly makes it up to fifty times faster. It has some of the best blocking features (you can block entire networks), will scan for both common and not-so-common holes and leaks, and has a firewall. There is a premium option that is great, but the free option is more than enough to protect your blog from most threats.
- Sucuri Security is a plugin from a company that specializes in auditing and internet security. It will incorporate many different blacklist engines onto your blog to protect it, and it has a ton of monitoring features available so you can know every last thing about the security and activity on your site. It is a fantastic all-around security application.
- Brute Force Login Protection is probably your best bet if you are being targeted with a botnet attack or, as the name suggests, a brute force attack. Since most of these types of attacks are automated, you need a good level of protection that will work automatically for you, and this plugin will block the IP address of a hacker who tries to log in too many times. You can even get an email when this happens so that you are aware of the frequency of attacks on your site.
Tip from Kevin: Stick to plugins found in the official WordPress directory.
You’ll be able to see when a plugin was last updated, whether it’s
compatible with the latest version of WordPress, how often its
developers answer “support” questions, and the star rating other users
have given it. Plus, all the plugins are free. I like free.
A final tip regarding this is to take an hour or so every few months
to review any applications you might be using on your blog. If they are
outdated, don’t hesitate to replace them. Cybersecurity evolves too
quickly to be loyal to something that no longer works.Use the Latest Version
If you are using WordPress or another hosting service which has multiple versions, make sure you are using the most recent one available. Hackers find a lot more security holes and problems in older versions of blogging platforms, and the hosts most likely do not support them nearly as much at their latest product.If you can upgrade, do it now. There are few disadvantages to upgrading after the first month (where they get the bugs out), and you can take advantage of the other features offered.
Protecting Your Blog on the Go
Many bloggers love to travel or work from outside the home, and this is a great thing. It allows for new perspectives and a faster, more consistent rate of production. However, there are many risks while blogging on the go, and you need to be prepared for them with the right knowledge and the right tools.Public Networks
When it comes to internet security in general, public networks are your worst enemy and a hacker’s best friend. While they are useful to many people who want to browse the internet for free, most people do not know the inherent lack of security many of them have.The biggest problem with a public network is that it is really easy for anyone to intercept your data uploaded or downloaded on the network. Think of your computer as a broadcast tower. Anyone with a receiver and the knowledge to use it can pick up the signal. Unfortunately, the receivers aren’t expensive, and they’re pretty easy for even novice hackers to use.
When your data is picked up in this manner, it can easily be used against you. Try to imagine if your passwords and usernames were just broadcast unencrypted for someone to pick up. If you log in without protection, that is what will happen. Heaven forbid you try online banking or blog-related financial transactions.
Use a VPN
The best way to counter the problems of public networks is to use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to defend yourself. What a VPN will do is connect your device via an encrypted connection to another server offsite. This connection can act as a tunnel and will mask your IP address, which will allow you a maximum level of security and privacy. Hackers won’t be able to know anything, even on a public network.There are many different VPNs out there, and many of them are specialized. Doing some research on the subject will help you find out which to use to ward off hackers on public networks as well as stay private. If you want a decent one, you will have to pay a subscription fee, but it is well worth it compared to the questionable free ones out on the market.
If you travel to other countries or have to access sensitive data, then another important thing about VPNs should be noted. The fact they mask IP addresses and make it appear as if you are browsing in a different country means that you can bypass government censorship if you are in a restrictive country. This is necessary for bloggers who are reporting on risky subjects.
Secure Your Smartphone
If you are travelling or even walking around town, you should make sure your smartphone is on you at all times and you can feel it. There is a huge market for stolen smartphones, and pickpockets love to make profits off of them.Your smartphone is likely connected to your blog, so if your smartphone gets stolen you need to make changing your password on it one of your first priorities. If a smartphone thief gets a blog to sell in addition to a new phone, you’ll have one more problem on your hands.
If you are worried about travelling with your smartphone, try leaving it in a safe place in the hotel if you don’t think you are going to need it, or place it on your person in a place a pickpocket won’t try to reach. One popular measure is to attach your smartphone to an arm strap that people like to use when working out and then wearing something over it.
Also, try to have some sort of verification measure set up on your phone so that not just anyone can open it. This can take the form of a passcode (that isn’t “1111”), a fingerprint verification, a voice command, or something else. Check to see what options your phone has available and pick the one that fits you and is the most secure.
Conclusion
To review, there are a lot of threats out there, but there are an equal number of defenses. You need to maintain an active and current website, have an adaptable and strong defense for all of your technology, and be even more wary when travelling.The final and best tip is to simply use common sense when using your blog. If something doesn’t look or sound right, don’t get involved. Check out any inconsistencies immediately. Don’t trust anyone.
Thank you for reading. I hope you have a better knowledge of the ways your blog is vulnerable and the ways you can protect yourself from hackers.🔺
__________________________________________
CONTACT US..!!
___________________________________________
https://www.facebook.com/Walkalone3933?ref=bookmarks
https://www.instagram.com/walk._.alone/
https://www.instagram.com/hackingtipsandstuff/
https://www.instagram.com/walk._.alone/
https://www.instagram.com/hackingtipsandstuff/
---------->Walk._.Alone<-----------